What is an elevator heating unit? What is an elevator heating unit? Elevator heating system of an apartment building
Types of heating elevators
Oddly enough, not even all plumbers servicing multi-story buildings know about heating elevators. At best, they have an idea that this device is installed in the system. But how it works and what function it performs is not known to everyone, not to mention ordinary people.
Therefore, let's eliminate this gap in knowledge about heating systems and examine this device in more detail.
What is an elevator?
In simple terms, an elevator is a special device related to heating equipment and performs the function of an injection or water-jet pump. No more, no less.
Its main task is to increase the pressure inside the heating system. That is, increase the pumping of coolant through the network, which will lead to an increase in its volume. To make it clearer, let's give a simple example. 5-6 cubic meters of water are taken from the supply water supply as a coolant, and 12-13 cubic meters enter the system where the apartments of the house are located.
How is this possible? And what causes the increase in coolant volume? This phenomenon is based on certain laws of physics. Let's start with the fact that if an elevator is installed in the heating system, it means that this system is connected to central heating networks through which hot water moves under pressure from a large boiler house or thermal power plant.
So the temperature of the water inside the pipeline, especially in extreme cold, reaches +150 C. But how can this be? After all, the boiling point of water is +100 C. This is where one of the laws of physics comes into force. At this temperature, water boils if it is in an open container where there is no pressure. But in the pipeline, water moves under pressure, which is created by the operation of the supply pumps. That's why it doesn't boil.
- Firstly, cast iron does not like large temperature changes. And if cast iron radiators are installed in apartments, they may fail. It's good if they just leak. But they can break, because under the influence of high temperatures, cast iron becomes brittle, like glass.
- Secondly, at this temperature of metal heating elements it will not be difficult to get burned.
- Thirdly, plastic pipes are now often used for piping heating devices. And the maximum that they can withstand is a temperature of +90 C (besides, with such figures, manufacturers guarantee 1 year of operation). This means they will simply melt.
Therefore, the coolant must be cooled. This is where an elevator is needed.
What is the elevator unit used for?
 Elevator unit connection diagram
Elevator unit connection diagram So we come to the question of why elevators are needed in a heating system?
These devices are designed to lower the temperature of the supplied water to the required temperature. And already cooled, it is supplied to the apartment heating system. That is, the coolant is cooled in the elevator. How?
Everything is quite simple. This device consists of a chamber where hot superheated water and water coming from the return circuit of the heating system are mixed. That is, the coolant from the boiler room is mixed with the coolant from the return line of the same house. This way, without taking a lot of hot water, you can obtain the required volume of coolant at the required temperature.
Are we losing temperature? Yes, we are losing, and the obvious cannot be denied here. But the coolant is supplied through a nozzle, which is much smaller than the diameter of the pipe supplying hot water to the house. The speed in this nozzle is so high due to the pressure inside the pipeline that the coolant is very quickly distributed throughout all risers. Therefore, no matter where the apartment is located, close or far from the distribution center, the temperature in the heating devices will be the same. Uniform distribution is thus ensured 100%.
Do you know what know-it-all plumbers sometimes do? They remove the nozzle and install metal dampers, thereby trying to manually regulate the flow rate of the coolant. It's good if they install it. And in some houses there are no dampers at all, and then the problems begin.
Apartments located closer to the elevator hub will have an African climate. Here, even in the most severe frosts, the windows are always open. And in distant apartments, especially corner ones, people wear felt boots and turn on electric heating appliances or a gas stove. They criticize everything under the sun, not suspecting that the companies servicing their home are to blame. Here is the result of ignorance and simple incompetence.
How does an elevator work?
The principle of operation of the elevator
 The principle of operation of the elevator
The principle of operation of the elevator The elevator unit is a fairly large container, somewhat similar to a pot. But this is not the elevator itself, although it is called that. This is a whole unit, which also includes:
- Dirt traps - after all, the water coming from the pipe is not entirely clean.
- Magnetic mesh filters - the unit must ensure a certain purity of the coolant so that batteries and pipes do not become clogged.
Having been purified, the hot water flows through the nozzle into the mixing chamber. Here it moves at high speed, as a result of which water is sucked in from the return circuit, which is connected to the mixing chamber on the side. The process of suction, or injection, occurs spontaneously. It is now clear that by changing the diameter of the nozzle, you can regulate both the volume of coolant supplied and its temperature at the exit from the elevator.
As you understand, for a heating system, an elevator is a pump and a mixer at the same time. And what is important - no electricity.
There is one more point that experts pay attention to - this is the ratio of the pressure inside the supply pipeline and the resistance of the elevator. This ratio should be 7:1. Only this ratio ensures the efficiency of the entire system.
But that's not all there is to efficiency. Pay attention to the fact that the pressure inside the system - and this is the supply and return circuits - must be the same. It is acceptable if it is a little less in the return. But if the difference is significant, for example, in the supply pipeline it is 5.0 kgf/cm2, and in the return pipeline it is below 4.3 kgf/cm2, this means that the pipeline system and heating devices are clogged with dirt.
 Connection diagram for an adjustable water-jet elevator
Connection diagram for an adjustable water-jet elevator Another possible reason is that during a major overhaul the pipe diameters were changed downward. That is, the contractor saved money in this way.
Is it possible to regulate the temperature of the coolant? It is possible, and for this it is better to use an adjustable water-jet type elevator.
The design of such a device includes a nozzle, the diameter of which can be changed. Sometimes the adjustment range, and this applies more to foreign analogues, is quite large, which is not so necessary. Domestic elevators have a smaller range shift, but, as practice has shown, this is enough for all occasions.
True, adjustable elevators are rarely installed in residential buildings. Their installation in public or industrial premises is much more effective. With their help, you can save up to 25% on heating costs just because they allow you to reduce the temperature at night, as well as on weekends and holidays.
Centralized heat supply systems are complex complexes. They transfer heat through main pipelines from suppliers to the end consumer. The heated coolant is supplied through distribution points and does not immediately fill the heating radiators inside the building. To equalize pressure and stabilize temperature, a special set of equipment is used - the elevator unit of the heating system. Let us dwell in detail on the design and operating principle of the elevator, consider the diagram and possible malfunctions.
Elevator unit of the heating system - what is it?
When touching the hot radiators in their own apartment, few people think about the complex path the heat from the boiler house or thermal power plant takes, as well as how a stable temperature is maintained. This is why it is difficult to get a clear answer to the question of what an elevator is in a heating system. Let's try to figure this out. Let's consider an enlarged diagram of the operation of a centralized heating system.
It includes:
- boiler houses or heating stations that heat and pump coolant;
- pipelines designed to supply thermal energy;
- pipelines through which the “return” circulates;
- numerous heat energy consumers;
- a system of branches from supply mains to specific buildings;
- thermal distribution units located inside buildings.
At an equal “return” temperature of 70 degrees Celsius, the standards provide for different operating modes of thermal power plants. In this case, the degree of heating of the medium supplied through the lines must correspond to one of the standard values - 95, 130 or 150 degrees Celsius. To safely supply heat through apartment radiators, there is a need to stabilize the pressure as well as the temperature of the water in the pipes. This is caused by a number of factors:
- different volumes of thermal energy consumption in each specific case. It is difficult to compare a multi-storey building with many apartments and a small store by this indicator;
- exceeding the temperature of the carrier in the lines as required by the standards. To feed heat exchange devices, it is necessary to reduce the temperature, which often exceeds the boiling point.
To ensure safe operating conditions for heating systems, it is unacceptable to supply water in a vapor state and under high pressure to heating devices. After all, touching heated radiators can cause a burn, and the release of steam during depressurization can lead to unpredictable consequences.
The elevator block is located mainly in the basements of buildings. It performs the following functions:
- cools incoming water to standard requirements;
- equalizes the coolant pressure in the pipes;
- promotes stable operation of central heating.
The unit is mounted between the supply pipe and the outlet pipe, which are connected in a special way. Piping elements must be installed - pressure control devices, thermometers, valves and valves.
The principle of operation of the elevator in the heating system and its design
The operating principle of the elevator unit of the heating system is based on cooling superheated water to the design level by mixing with colder water from the return line. The device then supplies media at the required temperature to the heating circuit of the building.
The elevator, designed to improve the efficiency of the heating system, performs the following functions:
- lowers the temperature of the coolant that flows through the inlet line to consumers;
- promotes the circulation of hot water throughout the kennel without the need for electrical power.
The device is widely used in distribution points to provide safe and efficient heating of large residential, industrial and administrative facilities. The node has a number of serious advantages:
- reliability. It is associated with the simplicity of the design, the absence of kinematic elements;
- low price. There are no expensive components and installation is easy;
- energy independence. There is no need to provide electricity for operation;
- efficiency. The use of an elevator device in conjunction with metering devices allows reducing coolant consumption by a third;
- durability. The elevator device does not require any adjustment work.
Along with the undeniable advantages, there are certain disadvantages:
- each heating circuit requires an individual calculation for installing an elevator unit;
- operation is carried out only in the presence of a pressure difference between the inlet and outlet lines;
- the difficulty of smoothly changing the parameters of a heating circuit equipped with an unregulated elevator.
Despite a number of disadvantages, the devices are quite widely used in public utilities. They operate stably when the hydraulic and thermal characteristics of the network fluctuate with the correct diameter of the conical nozzle.
The design of the elevator is quite simple. It is a kind of tee with flanges and includes the following elements:
- a discharge nozzle installed on the inlet line and supplying superheated water to the unit;
- a vacuum chamber located at the outlet of the tapering nozzle and connected by a flange to the “return” line;
- mixing zone, in which flows are combined and the temperature of the coolant decreases;
- a cone-shaped jet pipe through which mixed water moves into the heating circuit.
The unit is also equipped with shut-off valves and control devices. Correct calculation and selection of an unregulated design allows you to combine cold and hot flows, while achieving a mixing coefficient that varies in the range from two to five.
Today, designs have been developed and are in use that allow smooth adjustment of performance characteristics using an electric drive. This allows you to change the coolant temperature automatically by changing the nozzle parameters. The adjustable device consists of the following components:
- a drive mechanism that moves the throttle needle;
- a housing containing a cone-shaped nozzle;
- a throttle needle located in the conical part of the housing;
- a toothed roller that converts rotational motion into needle movement.
The design of the unit allows the use of a manual or electric drive. This allows you to smoothly regulate the water supply and, accordingly, change the temperature. By adjusting the cross-section of the conical section, the flow rate changes, allowing the temperature to gradually change. The use of an electric drive allows you to remotely control the process of adjusting parameters.
The method for calculating the conical part of the device and its diameter is carried out in accordance with the requirements of building regulations. A detailed algorithm for performing elevator calculations is widely presented in heating textbooks and specialized websites. It takes into account operating conditions taking into account the total volume of thermal energy consumed.

To perform calculations, it is necessary to determine the temperature values in different areas. Controlled areas:
- entrance to the elevator device;
- heating plant return pipe;
- pipes inside the building;
- return of the internal circuit.
You also need to know:
- the total amount of thermal energy required to maintain a comfortable temperature in a particular building;
- a set of parameters characterizing the laying of heating circuit pipes inside the house.
Based on the initial data, according to the formulas given in the regulatory manual, a calculation is performed. His technique is quite complex, so to determine the parameters of a critical device, it is advisable to use the services of professional designers.
To perform calculations yourself, you can use:
- ready-made software;
- online calculator;
- Excel program containing the necessary formulas.
When performing calculations to determine the required chamber diameter, it is necessary to calculate the square root of the total amount of mixed water and multiply the resulting value by a coefficient equal to 0.874. When selecting an elevator device, it is advisable to substitute different temperature values in order to assess how much its operating parameters will change.
Diagram of an elevator heating unit
As the schematic diagram shows, the elevator unit of the heating system consists of the following elements:
- supply line through which heated coolant is supplied from the boiler room or heating station;
- a return pipeline through which cooled water circulates, releasing thermal energy;
- valves that allow you to regulate the volume of transported coolant and are necessary for carrying out preventive or repair measures;
- a meter that records the amount of water supplied and necessary to pay for services;
- pressure gauges that monitor pressure in various sections of the pipeline and are necessary for monitoring;
- thermometers installed at the entrance to the elevator device, as well as at the outlet section of the unit and at the “return”;
- a dirt filter that carries out rough cleaning of the water entering the circuit from large impurities;
- an elevator device that mixes flows and ensures circulation of the medium.

The elevator unit is the main link of the thermal circuit. It is tied to communications using strapping elements.
Elevator in the heating system - main unit malfunctions
Despite the simplicity of the design, unexpected failures are possible in the operation of the unit. By paying attention to the values of pressure gauges installed in control zones, as well as temperature indicators, faults can be diagnosed:
- reducing the cross-section of pipelines. Associated with blockage from solid particles or dirt. The malfunction is determined by a decrease in pressure in the heating system;
- nozzle clogged. In this case, sharp pressure surges occur, which reach a maximum value when the conical part is completely destroyed;
- filter mesh element is clogged. It is determined by the increase in pressure in the circuit, at which the readings of the pressure gauges installed at the inlet and outlet of the mud filter differ;
- corrosion of the conical part. It causes a change in the size of the nozzle and manifests itself in the form of temperature changes. They can be easily determined by thermometer readings or battery temperature.
If breakdowns occur, a preventive inspection should be carried out and the condition of the nozzle assessed. If there are blockages, they should be removed and the pipes cleaned. Significant deviations in the dimensions of the conical part of the device can cause unbalancing of the heating circuit. In this case, the conical element must be replaced with a new nozzle corresponding to the design dimensions.
To summarize - what is an elevator heating unit and how necessary is it?
In the final part, I would like to emphasize the importance of the elevator for the proper operation of the central heating system. It is necessary to pay special attention to the cleanliness of the working surface and the conformity of the dimensions of the cone exposed to corrosion processes. The discrepancy between the characteristics disrupts the coolant circulation process. At the same time, there is a drop in temperature and hydraulic noise occurs. These factors cause serious inconvenience to residents.
Of course, heating is the most important life support system in any home. It can be found in any buildings that receive central heating. In such a system, elevator heating units are very important mechanisms.
What parts do they consist of, how do they function and, in general, what is an elevator heating unit in this article we will consider.
Elevator what is it
To understand and understand what this element is, it is best to go down to the basement of the building and see it with your own eyes. But if you have no desire to leave your home, then you can view the photo and video files in our gallery. In the basement, among the many gate valves, pipelines, pressure gauges and thermometers, you will definitely find this unit.
We suggest first understanding the principle of operation. Hot water is supplied to the building from the district boiler house, and cooled water is discharged.
This requires:
- Supply pipe– delivers hot coolant to the consumer;
- Return pipeline– performs work to remove the cooled coolant and return it to the district boiler room.

Several houses, and in some cases each one if the houses are large, are equipped with thermal chambers. They distribute coolant between houses, and also install shut-off valves that serve to cut off pipelines. Drainage devices can also be installed in the chambers, which are used to empty pipes, for example, for repair work. Further, the process depends on the temperature of the coolant.
In our country there are several main modes of operation of district boiler houses:
- Supply 150 and return 70 degrees Celsius;
- Respectively 130 and 70;
- 95 and 70.
The choice of mode depends on the latitude of residence. So, for example, for Moscow a 130/70 schedule will be sufficient, but for Irkutsk a 150/70 schedule will be needed. The names of these modes have the numbers of the maximum load of the pipelines. But depending on the air temperature outside the window, the boiler room can operate at temperatures of 70/54.

This is done to prevent overheating in the rooms and to make them comfortable to stay in. This adjustment is performed at the boiler room and is a representative of the central type of adjustment. An interesting fact is that in European countries a different type of regulation is performed - local. That is, adjustment takes place at the heat supply facility itself.
In this case, heating networks and boiler houses operate at maximum capacity. It is worth saying that the highest performance of boiler units is achieved precisely at maximum loads. comes to the consumer and is locally regulated by special mechanisms.
These mechanisms consist of:
- Outdoor and indoor temperature sensors;
- Servo drive;
- Actuator with valve.
Such systems are equipped with individual devices for metering thermal energy, thereby achieving great savings in monetary resources. Compared to elevators, such systems are less reliable and durable.
So, if the coolant has a temperature of no more than 95 degrees, then the main task is the high-quality physical distribution of heat throughout the system. To achieve these goals, manifolds and balancing valves are used.

But in the case when the temperature is above 95 degrees, it needs to be reduced a little. This is what elevators do in the heating system; they add chilled water from the return line to the supply pipeline.
Important. The process of adjusting the elevator unit is the simplest and cheapest mechanism; the main thing is to correctly calculate the heating elevator.
Features and Specifications
As we have already figured out, the elevator of the heating system is responsible for cooling the superheated water to a given value. This prepared water then enters.
This element improves the quality of operation of the entire building system and, when properly installed and selected, performs two functions:
- Mixing;
- Circulation.
Advantages of the elevator heating system:
- Simplicity of design;
- High efficiency;
- No electrical connection required.
Flaws:
- We need accurate and high-quality calculation and selection of a heating elevator;
- There is no way to regulate the outlet temperature;
- It is necessary to maintain a pressure difference between supply and return of around 0.8-2 bar.
Nowadays, such elements have become widespread in heating networks. This is due to their advantages, such as resistance to changes in hydraulic and temperature conditions. In addition, they do not require constant human presence.

Important. Calculation, selection and configuration of elevators should not be done with your own hands; this matter is best left to specialists, since a selection error can lead to big problems.
Design
The elevator consists of:
- Vacuum chambers;
- Nozzles;
- Jet elevator.
Among heating engineers there is a concept called piping an elevator unit. It consists of installing the necessary shut-off valves, pressure gauges and thermometers. All this is assembled and is a unit.
Important! Today, manufacturers sell elevators that, thanks to an electric drive, can adjust the nozzle. At the same time, it is possible to adjust the coolant flow automatically. But it is also worth noting that such equipment does not yet have a high degree of reliability.

Reliability for many years
Technological progress does not stop for a second. More and more new technologies are finding their application in heating buildings. There is one alternative to conventional elevators - this is equipment with automatic temperature control. They are considered to be more energy-saving and economical, but their price is higher. In addition, they cannot work without power supply, and periodically need a lot of power. What is better to use only time will tell.
Results
In this article we found out what an elevator is in a heating system, what it consists of and how it works. As it turned out, such equipment is widespread due to its undeniable advantages. There is no reason for utility companies to abandon them.

There are alternatives for this equipment, but they are distinguished by their high cost, lower reliability and energy efficiency, because they require electricity and periodic repairs to operate.
Reducing heat losses is the main task when planning district heating. To do this, even at the stage of heating the coolant, special conditions are created for its transportation: increased pressure, maximum temperature conditions. But in order for the distribution of hot water to reduce its heating level to the required level, an elevator heating unit is installed: the diagrams, operating principles and checks must strictly comply with the standards. Even though it is part of central heating, the average user should know how it works.
Purpose of the elevator unit
Even at the first stages of designing central heating, engineers were faced with the problem of conserving thermal energy due to the length of heating mains. To reduce heat losses, two main methods are used:
- Maximum thermal insulation of the pipe surface;
- Installation of elevator units in buildings.
The operating temperature in the external heating pipes is 150 or 130 degrees. It is prohibited to supply water to consumers at this temperature. That is why an adjustable elevator heating unit was developed. It is designed to mix hot and cold coolant flows in order to optimize its temperature. In addition, the pressure also decreases to an acceptable level.
For normal operation, an automatic elevator heating unit is installed in a pre-prepared room. For residential apartment buildings, this is the basement. Installation and further maintenance should only be performed by specialists. Any violation of the operating mode may lead to emergency situations. Installation of such a heating element in private houses is impractical. This is due to the fact that the boilers will not be able to provide the proper operating temperature. Therefore, it is used only for creating branched heating systems with a large length of external heat pipes.
Taking as a basis the operating principle of this elevator heating unit, it is possible to make a similar system for an autonomous system. But for this, two or three-way valves with thermostats are used.
Scheme of operation of the elevator unit

At first glance, the operating principle of the elevator unit of the heating system should be a rather complex system. However, in practice, a successful design has been developed, which in its technical characteristics is similar to a three-way mixing valve.
Structurally, it consists of the following elements:
- Inlet pipe. A coolant with a high temperature under maximum pressure flows through it;
- Return pipe. Necessary for connecting cooled water for further mixing with the hot flow;
- Nozzle. A key element of the diagram of elevator units of the heating system. Hot water enters it under pressure and creates a vacuum in the receiving chamber. As a result, the cooled coolant mixes with the heated one;
- Outlet pipe. Connects to the distribution pipeline system for further transportation of liquid to consumers.

In addition to it, the elevator unit of the central heating system must include additional elements. These include mud slides, shut-off valves and sensors. The latter are required for installation, since they help control the parameters of the entire system.
Having understood what an elevator heating unit is, you need to learn more about its types and methods of adjusting operating modes.
After checking the operation of the elevator unit and the entire heating system, you must definitely request an updated passport for the device. It indicates the initial characteristics and the actual ones after control checks.
Types of elevator heating units
This heating diagram for the elevator unit does not reveal the temperature control mechanism. And this is the main way to optimize thermal energy consumption depending on external factors - the temperature outside, the degree of thermal insulation of the house, and so on. To do this, a special cone-shaped rod is installed in the nozzle. Gears ensure its connection with the valve. By adjusting the position of the rod, the throughput of the nozzle changes.
Depending on the installed equipment, there are two types of adjustable elevator heating units:
- Manual method. The valve is rotated using the traditional method. In this case, the responsible employee must monitor the readings of pressure gauges and thermometers of the system;
- Auto. A servo drive is installed on the valve pin, which is connected to temperature and pressure sensors. Depending on the established indicators, movements of the rod are performed.
A typical drawing of an elevator unit should include not only the required elements, but also the operational characteristics of the system. And for this you need to calculate the parameters. Such work is carried out only by specialized design organizations, as it requires taking into account all factors.
Installing an adjustable elevator unit for heating in combination with a thermal energy consumption meter will save up to 30% of hot coolant consumption.
Installation features and testing

It is worth immediately noting that installation and testing of the operation of the elevator unit and heating system is the prerogative of representatives of the service company. Residents of the house are strictly prohibited from doing this. However, knowledge of the layout of the elevator units of the central heating system is recommended.
During design and installation, the characteristics of the incoming coolant are taken into account. The branching of the network in the house, the number of heating devices and the operating temperature are also taken into account. Any automatic elevator unit for heating consists of two parts.
- Adjusting the intensity of the flow of incoming hot water, as well as measuring its technical indicators - temperature and pressure;
- Directly the mixing unit itself.
The main characteristic is the mixing ratio. This is the ratio of the volumes of hot and cold water. This parameter is the result of precise calculations. It cannot be a constant, since it depends on external factors. The installation must be carried out strictly according to the diagram of the elevator unit of the heating system. After this, fine tuning is done. To reduce errors, a maximum load is recommended. This way the water temperature in the return pipe will be minimal. This is a prerequisite for precise control of the automatic valve.
After a certain period of time, scheduled checks of the operation of the elevator unit and the heating system as a whole are necessary. The exact procedure depends on the specific scheme. However, you can draw up a general plan that includes the following mandatory procedures:
- Checking the integrity of pipes, shut-off valves and devices, as well as compliance of their parameters with passport data;
- Adjustment of temperature and pressure sensors;
- Determination of pressure loss during coolant passage through the nozzle;
- Calculation of the displacement coefficient. Even for the most accurate heating scheme for an elevator unit, equipment and pipelines wear out over time. This amendment must be taken into account when setting up.
After this work has been completed, the automatic central heating elevator unit must be sealed to prevent tampering.
You cannot use homemade schemes of elevator units for central heating systems. They often do not take into account the most important characteristics, which can not only reduce operational efficiency, but also cause an emergency.
Premises requirements
In the vast majority of cases, mixing units are installed in the basement of the building. To perform its functions, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of the room - seasonal changes in temperature and humidity.
There are a number of requirements for these indicators, the fulfillment of which is mandatory. This especially applies to elevator units of the central heating system with installed automatic servos:
- The room temperature should not fall below 0°C;
- To prevent the appearance of condensation on the surface of the pipes, an exhaust ventilation system is installed;
- A separate switchboard must be installed for electrical appliances. It is recommended to provide an autonomous power supply in case of an emergency power outage.
However, in fact, it is rare to see adherence to these rules. As a result, even for the most effective drawing of an elevator unit, its practical implementation may differ significantly. That is why alternative schemes for mixing coolant flows have appeared.
Some new apartment buildings connected to central heating do not have a heating circuit with an elevator unit. To install it, you need to contact the management company.
Other options for thermal units

Based on the basic principle of operation of the elevator unit of the heating system, alternative methods have been developed to maintain the desired temperature level in the pipes for users. Their difference from the traditional scheme lies in the presence of a complex electronic control system.
The first thing the developers of this unit paid attention to was the optimal flow of hot water. Therefore, a thermal energy meter must be installed at the inlet pipe. It makes it possible not only to see the volume of coolant entering the home system, but can also automatically calculate its cost and transmit the data to the management company.
The installed pumps allow you to control the speed of passage of the coolant through the pipes. This is necessary to reduce the error when mixing fluid flows in the nozzle. To do this, temperature sensors are mounted on the inlet and return pipes. If the water heating level is less than the set one, the return pump stops working. To increase the volume of hot coolant, the corresponding pumping equipment is activated.
Multi-storey buildings, high-rise buildings, administrative buildings and many different consumers provide heat from combined heat and power plants or powerful boiler houses. Even a relatively simple autonomous system in a private home is sometimes difficult to adjust, especially if errors were made during the design or installation. But the heating system of a large boiler house or thermal power plant is incomparably more complex. There are many branches leaving the main pipe, and each consumer has different pressure in the heating pipes and the amount of heat consumed.
 Pipe lengths vary and the system must be designed so that the furthest consumer receives sufficient heat. It becomes clear why there is coolant pressure in the heating system. Pressure moves water along the heating circuit, i.e. created by the central heating line, it plays the role of a circulation pump. The heating system must not allow imbalance when the heat consumption of any consumer changes.
Pipe lengths vary and the system must be designed so that the furthest consumer receives sufficient heat. It becomes clear why there is coolant pressure in the heating system. Pressure moves water along the heating circuit, i.e. created by the central heating line, it plays the role of a circulation pump. The heating system must not allow imbalance when the heat consumption of any consumer changes.
 In addition, the efficiency of heat supply should not be affected by the branching of the system. In order for a complex centralized heating system to operate stably, it is necessary to install either an elevator unit or an automated heating system control unit at each facility to eliminate mutual influence between them.
In addition, the efficiency of heat supply should not be affected by the branching of the system. In order for a complex centralized heating system to operate stably, it is necessary to install either an elevator unit or an automated heating system control unit at each facility to eliminate mutual influence between them.
 Heating engineers recommend using one of three temperature modes for boiler operation. These modes were initially calculated theoretically and underwent many years of practical application. They ensure heat transfer with minimal losses over long distances with maximum efficiency.
Heating engineers recommend using one of three temperature modes for boiler operation. These modes were initially calculated theoretically and underwent many years of practical application. They ensure heat transfer with minimal losses over long distances with maximum efficiency.
Thermal conditions of a boiler room can be defined as the ratio of the supply temperature to the return temperature:

 In real conditions, the mode is selected for each specific region based on the winter air temperature. It should be noted that high temperatures, especially 150 and 130 degrees, cannot be used for heating premises in order to avoid burns and serious consequences in case of depressurization.
In real conditions, the mode is selected for each specific region based on the winter air temperature. It should be noted that high temperatures, especially 150 and 130 degrees, cannot be used for heating premises in order to avoid burns and serious consequences in case of depressurization.
 The water temperature exceeds the boiling point and it does not boil in the pipelines due to the high pressure. This means that it is necessary to reduce the temperature and pressure and ensure the necessary heat extraction for a particular building. This task is assigned to the elevator unit of the heating system - special heating equipment located in the heat distribution point.
The water temperature exceeds the boiling point and it does not boil in the pipelines due to the high pressure. This means that it is necessary to reduce the temperature and pressure and ensure the necessary heat extraction for a particular building. This task is assigned to the elevator unit of the heating system - special heating equipment located in the heat distribution point.
Design and principle of operation of a heating elevator
 At the entry point of the heating network pipeline, usually in the basement, a node that connects the supply and return pipes catches your eye. This is an elevator - a mixing unit for heating a house. The elevator is manufactured in the form of a cast iron or steel structure equipped with three flanges. This is an ordinary heating elevator; its operating principle is based on the laws of physics. Inside the elevator there is a nozzle, a receiving chamber, a mixing neck and a diffuser. The receiving chamber is connected to the “return” using a flange.
At the entry point of the heating network pipeline, usually in the basement, a node that connects the supply and return pipes catches your eye. This is an elevator - a mixing unit for heating a house. The elevator is manufactured in the form of a cast iron or steel structure equipped with three flanges. This is an ordinary heating elevator; its operating principle is based on the laws of physics. Inside the elevator there is a nozzle, a receiving chamber, a mixing neck and a diffuser. The receiving chamber is connected to the “return” using a flange.
 Superheated water enters the elevator inlet and passes into the nozzle. Due to the narrowing of the nozzle, the flow speed increases and the pressure decreases (Bernoulli's law). Water from the return line is sucked into the area of low pressure and mixed in the mixing chamber of the elevator. The water reduces the temperature to the desired level and at the same time the pressure decreases. The elevator works simultaneously as a mixer. This is briefly the principle of operation of an elevator in the heating system of a building or structure.
Superheated water enters the elevator inlet and passes into the nozzle. Due to the narrowing of the nozzle, the flow speed increases and the pressure decreases (Bernoulli's law). Water from the return line is sucked into the area of low pressure and mixed in the mixing chamber of the elevator. The water reduces the temperature to the desired level and at the same time the pressure decreases. The elevator works simultaneously as a mixer. This is briefly the principle of operation of an elevator in the heating system of a building or structure.
Thermal unit diagram
 Adjustment of the coolant supply is carried out by the elevator heating units of the house. The elevator is the main element of the heating unit and needs piping. The control equipment is sensitive to contamination, so the piping includes dirt filters that are connected to the “supply” and “return”.
Adjustment of the coolant supply is carried out by the elevator heating units of the house. The elevator is the main element of the heating unit and needs piping. The control equipment is sensitive to contamination, so the piping includes dirt filters that are connected to the “supply” and “return”.
The elevator harness includes:
- mud filters;
- pressure gauges (inlet and outlet);
- temperature sensors (thermometers at the elevator inlet, outlet and return);
- valves (for preventive or emergency work).
 This is the simplest circuit option for adjusting the temperature of the coolant, but it is often used as the basic device of a thermal unit. The basic elevator heating unit for any buildings and structures provides regulation of the temperature and pressure of the coolant in the circuit.
This is the simplest circuit option for adjusting the temperature of the coolant, but it is often used as the basic device of a thermal unit. The basic elevator heating unit for any buildings and structures provides regulation of the temperature and pressure of the coolant in the circuit.
The advantages of using it for heating large objects, houses and high-rise buildings:

But while there are undeniable advantages of using an elevator for heating systems, the disadvantages of using this device should also be noted:

Elevator with automatic adjustment
 Currently, elevator designs have been created in which the nozzle cross-section can be changed using electronic adjustment. This elevator has a mechanism that moves the throttle needle. It changes the lumen of the nozzle and as a result the coolant flow changes. Changing the lumen changes the speed of water movement. As a result, the mixing ratio of hot water and water from the “return” changes, thereby achieving a change in the temperature of the coolant in the “supply”. Now it’s clear why water pressure is needed in a heating system.
Currently, elevator designs have been created in which the nozzle cross-section can be changed using electronic adjustment. This elevator has a mechanism that moves the throttle needle. It changes the lumen of the nozzle and as a result the coolant flow changes. Changing the lumen changes the speed of water movement. As a result, the mixing ratio of hot water and water from the “return” changes, thereby achieving a change in the temperature of the coolant in the “supply”. Now it’s clear why water pressure is needed in a heating system.
The elevator regulates the flow and pressure of the coolant, and its pressure drives the flow in the heating circuit.
Main malfunctions of the elevator unit
Even such a simple device as an elevator unit may not work correctly. Malfunctions can be determined by analyzing pressure gauge readings at control points of the elevator unit:

Switchgears
The elevator unit with all its piping can be thought of as a pressure circulation pump, which supplies coolant to the heating system under a certain pressure.
If the facility has several floors and consumers, then the most correct solution is to distribute the total coolant flow to each consumer.
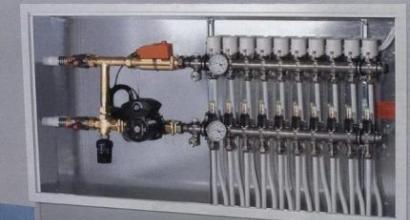
 To solve such problems, a comb is designed for the heating system, which has another name - a collector. This device can be represented as a container. The coolant flows into the container from the elevator outlet, which then flows out through several outlets, with the same pressure.
To solve such problems, a comb is designed for the heating system, which has another name - a collector. This device can be represented as a container. The coolant flows into the container from the elevator outlet, which then flows out through several outlets, with the same pressure.
 Consequently, the distribution comb of the heating system allows the shutdown, adjustment, and repair of individual consumers of the facility without stopping the operation of the heating circuit. The presence of a collector eliminates the mutual influence of the heating system branches. In this case, the pressure in corresponds to the pressure at the elevator outlet.
Consequently, the distribution comb of the heating system allows the shutdown, adjustment, and repair of individual consumers of the facility without stopping the operation of the heating circuit. The presence of a collector eliminates the mutual influence of the heating system branches. In this case, the pressure in corresponds to the pressure at the elevator outlet.
Three way valve
If it is necessary to divide the coolant flow between two consumers, a three-way heating valve is used, which can operate in two modes:

 A three-way valve is installed in those places in the heating circuit where it may be necessary to divide or completely shut off the flow of water. The tap material is steel, cast iron or brass. Inside the faucet there is a shut-off device, which can be ball, cylindrical or conical. The tap resembles a tee and, depending on the connection to the heating system, can work as a mixer. Mixing proportions can be varied within wide limits.
A three-way valve is installed in those places in the heating circuit where it may be necessary to divide or completely shut off the flow of water. The tap material is steel, cast iron or brass. Inside the faucet there is a shut-off device, which can be ball, cylindrical or conical. The tap resembles a tee and, depending on the connection to the heating system, can work as a mixer. Mixing proportions can be varied within wide limits.
The ball valve is mainly used for: 
- adjusting the temperature of heated floors;
- adjusting battery temperature;
- distribution of coolant in two directions.
There are two types of three-way valves - shut-off and control valves. In principle, they are almost equivalent, but with three-way shut-off valves it is more difficult to regulate the temperature smoothly.