All about heating a private home. Do-it-yourself heating of a private house: video, diagrams
Water heating is the most common option for heating a private home. The location of the main structural elements determines the type of system and the features of its operation. A competent choice of piping layout is the key to heating efficiency and occupant comfort.
Classification of water heating systems
Water heating systems are complex engineering systems with many varieties. The coolant in them is water or aqueous solutions for special purposes. Depending on the configuration of the systems, they are classified according to the following parameters:
- by the method of coolant circulation;
- by the presence of contact with atmospheric air;
- according to the power supply diagram of the devices;
- according to the location of main pipelines.
 Heating scheme with natural circulation of open type. 1 - boiler; 2 - expansion tank; 3 radiator; 4 - hot outlet of the boiler heat exchanger, goes strictly vertically to the expansion tank; 5 - main supply pipe; 6 - riser; 7 — main return pipe; 8 - ball valve; 9 - drain with ball valve for coolant discharge
Heating scheme with natural circulation of open type. 1 - boiler; 2 - expansion tank; 3 radiator; 4 - hot outlet of the boiler heat exchanger, goes strictly vertically to the expansion tank; 5 - main supply pipe; 6 - riser; 7 — main return pipe; 8 - ball valve; 9 - drain with ball valve for coolant discharge
The first way to organize the movement of coolant through the system is natural circulation. This option allows you to ensure the operation of the heating without being dependent on the availability of electricity. Circulation is carried out due to gravitational forces. The liquid heated in the boiler rises due to a decrease in density, enters the radiators, gives off heat and returns to the boiler.
 Closed forced circulation heating circuit. 1 - boiler; 2 — air vent; 3 - pressure gauge; 4 — safety valve (numbers 2, 3, 4 constitute the safety group); 5 - expansion tank; 6 - radiator; 7 — coarse filter; 8 - drain; 9 - circulation pump; 10 - ball valve
Closed forced circulation heating circuit. 1 - boiler; 2 — air vent; 3 - pressure gauge; 4 — safety valve (numbers 2, 3, 4 constitute the safety group); 5 - expansion tank; 6 - radiator; 7 — coarse filter; 8 - drain; 9 - circulation pump; 10 - ball valve

The figure shows a single-pipe system with vertical distribution. Different risers show different types of device connections.

The diagram below shows the typical configuration of a two-pipe system with vertical wiring.
 Single-pipe pressure heating system: 1 - boiler; 2 - security group; 3 — radiators; 4 - needle valve; 5 - expansion tank; 6 - drain; 7 - water supply; 8 - filter; 9 - pump; 10 - ball valves
Single-pipe pressure heating system: 1 - boiler; 2 - security group; 3 — radiators; 4 - needle valve; 5 - expansion tank; 6 - drain; 7 - water supply; 8 - filter; 9 - pump; 10 - ball valves
The simplest one-pipe system with horizontal wiring involves the sequential passage of coolant through all devices within one floor.
 Manifold circuit: 1 - boiler; 2 - expansion tank; 3 - supply manifold; 4 — heating radiators; 5 — return manifold; 6 - pump
Manifold circuit: 1 - boiler; 2 - expansion tank; 3 - supply manifold; 4 — heating radiators; 5 — return manifold; 6 - pump
A two-pipe horizontal system can have perimeter or radial (collector) wiring. In the first case, pipes are laid along the perimeter of the room, gradually powering all devices; in the second, each heating device has a separate supply line.

Radial distribution pipes are laid in the floor screed along the shortest routes to each radiator. Moreover, their configuration resembles rays emanating from one source - the distribution manifold. This was the reason for the appearance of the corresponding name.
Collectors in modern interiors of private houses are often neatly hidden in special cabinets, which allows you to preserve the aesthetics of the room and hide the elements of setting up and regulating the system.
Radiator connection types
The connection diagram for heating devices is selected based on the selected structure of the heating system, ease of installation and maintenance, as well as interior features.
 1 - Two-pipe wiring. 2 — Single-pipe wiring
1 - Two-pipe wiring. 2 — Single-pipe wiring
The figure shows the main options for connecting radiators, typical for vertical systems.
 A - lateral connection; B - diagonal; B - bottom connection
A - lateral connection; B - diagonal; B - bottom connection
An analysis of the circuits that are most often found in horizontal systems shows that the type of connection of radiators has a significant impact on the efficiency of heat transfer. Before giving preference to a more convenient installation option, you should think carefully about whether you are ready to sacrifice some of the precious heat.
As can be seen from everything stated above, the choice of a water heating scheme for a private house is associated with the need for a thorough analysis of many options. In addition to the main varieties described, there is an even more detailed classification. Consultation with a qualified specialist will help you quickly navigate all the diversity, take into account the existing nuances and achieve the best results.
Reading time ≈ 19 minutes
For those who live outside the city or just in a small town or village, it will be quite useful to know how to properly install heating in a private home. The approach here is very important from both a financial and practical point of view, that is, do I have enough money to carry out the project and do I need one or another heating method to provide heat in all living rooms of the building. Of course, these are questions of a personal nature, and now we will look at the main directions that are used in the private sector, and quite successfully.
Three main systems for heating a private home
Installation of radiator heating in a private house
There are many ways to heat houses in the private sector, but recently three of them can be called the most popular:
- Radiator heating.
- Water heated floor system.
- Combination of radiator heating and water heated floor system.
Maybe someone will say that the most popular at the moment is stove heating. Maybe. However, we will still talk about autonomous water heating and methods of its installation. But before that, you need to pay a little attention to the elements of the heating systems from which the circuit is assembled in any case.
Devices and elements used for heating

Aluminum radiators of different sizes
Today, if we don’t talk about their configuration, there are three types of radiators that differ in metal and these are:
- cast iron;
- steel;
- aluminum;
- bimetal
If we are talking about the private sector, then heating can only be autonomous and only 0.1% of private houses are connected to centralized boiler houses. These are the houses that were once built by enterprises for their workers, but were bought over time, and centralized heating still remains in some places, although not all of them have it.
- This means that cast iron radiators are no longer needed, since they take too long to heat up and require a large amount of water, which is not at all suitable for autonomy - too many expenses.
- Steel batteries, both sectional and panel (non-removable), are excellent for a private home - they have good heat transfer and a pleasant appearance, but they begin to rust and fail the fastest.
- Aluminum radiators are intended exclusively for autonomous heating and there are two reasons for this: firstly, they will not withstand very high pressure and, secondly, special additives must be added to the coolant, which is impossible with a centralized water supply.
- , this is an ideal option both for the private sector and for multi-storey buildings. They withstand the highest possible pressure, but in this case we are not interested in this, but they have excellent heat transfer, and the service life is almost equal to cast iron, that is, if for cast iron it is 30-35 years, then for bimetal it is 25-30 years .

Cross-linked polyethylene pipe layers
For a heated floor system, not even according to the instructions, but by default, a pipe made of high quality cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) should be used. The problem here is that, firstly, it is an expensive material, although a good one, and, secondly, when pouring the second layer of screed, which is done on top of the heated floor system, the pipes need to be filled with water so as not to flatten them with the solution (this causes certain inconveniences). But practice has shown that cheaper metal plastic is excellent for this purpose, only it must be seamless - this ensures its strength. From my own experience, I can say that underfloor heating systems made of metal plastic, installed 10-15 years ago by me personally, are still functioning successfully.

Setting up a double-circuit convection gas boiler
If we talk about boilers for water heating, they can be:
- gas;
- electrical;
- diesel;
- solid fuel.
Be that as it may, gas units are certainly the best and there are several reasons for this. Firstly, double-circuit models provide hot water supply for the home without installing an indirect heating boiler, secondly, such units can be not only convection, but also condensation (low temperature), energy-dependent and non-volatile, and modern models must have a built-in circulation pump . Gas boilers of any type are also equipped with built-in groups of various equipment: for automatic adjustment of temperature conditions and a safety group.
Unfortunately, not every area has the ability to connect to a gas main, and then most often they use electric boilers of various types, but in 99% of cases, these are heating elements, although some prefer electrode or induction models. But even here, not everything is so smooth - in the distance from the city, due to old transformers, sometimes there is not enough voltage to ensure normal operation of the electrical unit, and that’s when diesel or solid fuel boilers are purchased. Of course, this is a personal matter for everyone, but a wood-burning boiler wins over a diesel one for several reasons. Firstly, solar fuel is more expensive than firewood, secondly, firewood does not require nozzles, which a diesel engine cannot do without, and thirdly, solid fuel boilers are much cleaner to operate (no soot or unpleasant odor).
Advantages and disadvantages of water heating

Integrated water heating system in the private sector
To begin with, as always, about the positive qualities of water heating systems:
- First of all, there is no need for daily cleaning and lighting of the stove.
- The microclimate can be adjusted in each room individually.
- You can leave home even for a month, leaving the boiler in the on position - it will work in the specified mode.
- Aesthetics of installation, both radiator and floor circuits.
- You don’t have to worry about storing fuel every year for the winter.
Of course, this method also has its downsides:
- High cost of equipment (boiler, radiators, pipes).
- In some cases, water leaks are possible in the radiator circuit.
- If you do not use the heating system in winter, there is a danger of defrosting.
As you can see, water heating has many more advantages than disadvantages, and this is not surprising - after all, such designs are a child of scientific and technological progress. In addition, this type of coolant is by far the cheapest, and therefore the most profitable. If you calculate all the costs as a whole, then the cost of stove heating, taking into account the time spent on it, will not be much lower at its price.
Radiator heating
You can, of course, talk about a radiator heating system in a general sense, like it’s convection heating from appliances distributed throughout the house and the like, but this is meaningless information, since everyone knows about it. Here it is important to highlight other factors, such as the number of pipes for the coolant, their location and the method of connecting heating devices to them.
Differences between single-pipe radiator circuits

Single-pipe heating system with natural circulation
Many people in private houses, especially small ones, prefer “one-pipe” and this is quite logical - installation is somewhat cheaper than for two-pipe wiring. Although it is cheaper only for small houses, for a large building this is already a controversial issue. The essence of the coolant movement here is as follows - it moves sequentially through all radiators, and having reached the last one, it returns to the boiler. In addition, such systems, compared to two-pipe systems, are easier to install, but this is only one side of the coin.
The fact is that the water, passing through each battery, becomes colder and colder, and often the very last device hardly heats up - it is almost impossible to correct this situation. The more points, the greater the cooling of the water, although this is somewhat compensated by the circulation pump, which does not allow the coolant to cool so quickly. For this reason, they try to make the plots as short as possible, in any case, a maximum of 30 m, and this is not always enough even for an average house. But, be that as it may, such systems “take place.”
Horizontal connection

Horizontal connection a) bottom; b) diagonal
The horizontal heating scheme in a private house is very convenient for one-story buildings, but here, in fact, there are three ways to install radiators. The two most popular are shown in the image above, that is, the pipe is laid near the floor, and radiators are connected to it using elbows. This is the most effective way to save coolant energy for a horizontal connection, that is, with this method the water cools less and the last point is still hot, although, of course, not as hot as the first two or three.
In addition, pay attention to the diagonal connection, it depends on the direction of water movement, that is, first the top, then the bottom - this is how the heating devices warm up best, since the sections are filled evenly. That is, with sufficient pressure, the coolant does not immediately fall down the first section, but is distributed further - from the vertical pipe of the device down along the ribs. With a lower connection, the upper part of the radiator is often colder, since the water movement mainly occurs along the lower pipe of the device, only slightly affecting the upper zone of the ribs.

The principle of this system is “from radiator to radiator”
Also, for horizontal wiring, the principle “from radiator to radiator” is sometimes practiced. This is when the coolant, having passed through one radiator, immediately enters the next one, that is, such a circuit does not provide for a separate pipe, but is itself a highway. If one battery is removed, the entire system becomes inoperable because it interrupts the flow. Of course, there is no dispute, this is the most economical of all possible options, because it will require a minimum number of pipes to connect the points to each other. But the heat loss for remote points here is very strong and I myself had to deal with the fact that the owners asked to redo such a scheme.
Vertical layout

Vertical distribution of radiators in the heating system is necessary for several floors
This type of wiring, as in the diagram above, is used in multi-storey buildings and a striking example of this is “Stalinka”, “Khrushchev” and “Brezhnevka”. This principle was adopted by the owners of two-story private houses and it must be said that it works, if only because no one turns the flow of water instead of a pipe through their own battery. The connection in this case is very similar to the horizontal one, but without diagonals, that is, it is either bottom or side. This, of course, is a big drawback and most often it is necessary to install an additional circulation pump.
This additional draft is especially important when the house is divided into two wings - heating on the side of the boiler is normal, but in the wing next to it it is cold. But here you need to be careful - if the power of the circulation pump installed in the adjacent wing exceeds the power of the pump integrated into the boiler, then everything will be exactly the opposite. This means that the coolant will flow out to the adjacent wing, and the wing in which the boiler is installed will turn out to be cold. In addition, if there are a large number of radiators, balancing valves are installed on them, which allow the supply to be evenly distributed to all points. All these are the costs of “single-tube” devices, but, I repeat, people use them quite successfully.
Leningradka system

Leningradka wiring system
Firstly, “Leningradka” is not know-how, but an ordinary single-pipe system of a horizontal type, but without a circulation pump, but with a pipe slope, due to which circulation occurs. Secondly, such a layout does not allow more than three radiators and is only suitable for small houses, for example, a room-bedroom-kitchen, so there won’t even be enough left for a bath. If a circulation pump appears on the return, then do not be mistaken - this is no longer a “Leningrad”, but the most common single-pipe system with forced supply of coolant.
One-pipe wiring. Is it as cheap as it seems?
Two-pipe heating system
You need to figure out how to install heating in a private home yourself and do it correctly, that is, without errors during installation. If we combine all the methods of such wiring together, we can say that these are two pipes, where hot water is supplied through one, and through the other the cooled liquid flows into the boiler for further heating. Radiators are inserted between these two circuits; the coolant, having passed through each of them, is immediately discharged into the return line. In fact, the number of heating devices here is not limited and until the liquid in the pipe cools down due to the distance, all radiators under certain conditions will have an equal chance of temperature control.
Such systems can be either with natural or forced circulation and have three types of device connections:
- Top connection.
- Bottom connection.
- Collector (radial) connection.
Top Wiring Systems

Top-mounted systems are more suitable for natural circulation
Numbering in the image:
- Heating boiler.
- Main riser.
- Coolant supply wiring.
- Supply risers.
- Return risers.
- Main return.
- Expansion tank.
In the top image you see the installation of heating with overhead wiring - this design is visually familiar, perhaps, to every adult, and hardly anyone is delighted with the pipe running near the ceiling or directly above the radiators. But this is a forced, but unusually effective option for the natural circulation of coolant, which was practiced in those days when they did not even think about circulation pumps. This method is still practiced for solid fuel boilers in our time, because it is not always possible to install a pump for forced supply.
The essence of this method is as follows: water is heated in boiler No. 1 and, naturally, following the laws of physics, it expands, therefore, rises through the main riser No. 2. The coolant continues along inclined bed No. 3. The slope is 0.01%, that is, it is 10 mm per linear meter. From the sun lounger, hot water enters risers No. 4, where the radiators are embedded, and after passing through the radiator, the coolant is discharged first into return riser No. 5 (this is for several floors), and then enters the main return pipe No. 6. This is the end of the cycle - along a flat return line, where the same slope (10 mm per linear meter) water is again sent to the boiler for heating and the start of a new cycle. In case of overheating, which often happens in unregulated boilers, the coolant rises into the expansion tank without causing any harm to the system.
This wiring is very convenient; the radiators on it have a diagonal connection, therefore, they warm up completely, without “dead” zones. A natural circulation system is suitable for use in the private sector, but not only for one floor - it can be equipped with up to three floors, but then the boiler will have to be raised to the 2nd or 3rd floor. In this case, the height of the heater reduces the need for high pressure injection, therefore, the higher the boiler, the larger the area that can be heated.
Bottom-wired systems

Bottom wiring for forced coolant circulation
In this case, the principle of supply and discharge of coolant remains the same as with natural circulation, but the presence of a pump (integrated into the boiler or additional) allows the supply circuit to be mounted below. This makes it possible to use closed pipes - they are filled with screed, hidden under drywall or recessed in grooves under plaster. Most often in such cases, the bottom connection of radiators is used to minimize the visibility of the pipes, but this is not important - the connection can also be lateral or diagonal, depending on the need.
But if there are a lot of radiators, heat loss cannot be avoided in any case, since the circuit will have to be extended. That is, if the first points on a segment of ten meters heat up by 100% or a little less, then along the pipe the heating will still drop due to the distance. To some extent, these losses are compensated by a larger feed diameter, for example, if the bends are made PPR Ø 20 mm, then the contour itself is PPR 25 mm or even PPR 32 mm. But such a measure is only partial and cannot evenly distribute heat to all points. Therefore, balancing valves are installed on the first radiators - these are essentially shut-off valves, only more precise, regulating the flow of coolant.
A huge advantage in this case is that the contour does not need a slope - it is usually mounted along a horizontal line, and sometimes even with a counter-slope. Another very important point: if it is planned to install an additional circulation pump, then it is installed only on the return line - it works most effectively on suction, and not on push. An expansion tank is also installed in such systems, but of the membrane type - it serves as an auxiliary device for the integrated circulation pump, creating pressure. In case of overheating, the boiler has a safety group with a blast valve.
Systems with collector (beam) wiring

Manifold wiring of radiators in a private residential building
No matter how good a two-pipe heating system is, nevertheless, there will be heat loss even with a circulation pump - this mainly depends on the length of the circuit and the longer it is, the more losses the outer radiators suffer. Of course, the way out is mainly balancing valves, but setting them up is not so easy, especially for a person who has never worked with heating - too much time is spent on adjustment.
Therefore, in a large house where there are many heating devices, the method of collector or radial radiator wiring is sometimes used. This does not mean that each battery is connected separately from the collector - one comb channel usually works for a group of heating devices. In such cases, losses are minimal, although sometimes it is also necessary to use balancing valves. The main disadvantage of such a layout is the large number of pipes, and this is not only a financial, but also a technical problem - the more pipes, the more difficult it is to lay them, since everything needs to be disguised.
There is another wiring option, very similar to the lower one in technology, but differing in the connection order. You can watch it in the video below. This is Tichelman's scheme. I deliberately omitted its description, since it is much clearer in the video.
Three radiator wiring diagrams
Warm floor
The underfloor heating system is mainly a privilege of the private sector, since it requires exclusively autonomous heating. Of course, there are a few cases of residents of multi-storey buildings refusing the services of a centralized boiler house, but the red tape that lies behind all this does not in any way contribute to enthusiasm.

Laying a pipe with a single (left) and double (right) snake
First, let's look at the methods of laying the heating circuit of a heated floor and at the top you see a single (left) and double (right) snake. From the picture it immediately becomes clear that the first method is bad, since the heating of the floors will be uneven, and this is simply unpleasant for the feet, although the room can warm up completely. Double laying distributes heat evenly over the entire floor area.

Spiral pipe laying
Of course, in most cases, this is not a square, but a round figure, but the principle of laying does not change from this - first, towards the center, the feed is laid, and then returned to the starting point to the collector. This is the most effective method for installing a heated floor system and is used in approximately 80% of cases. A snake is most often needed in hard-to-reach places: under the stairs, behind the bar counter, and so on.

Mounting methods: on brackets (left), on clamps (right)
To fix both polyethylene and metal-plastic pipes so that they do not move out of place, use fastenings in the form of brackets or clamps, but at the same time adhere to a pitch of 200 mm with any laying configuration. Foil must be placed under the contour (most often it is 2-mm foam foil), and if necessary, the bottom screed is insulated).

Wiring of the heated floor system from the collectors
A pipe that is filled with a screed (polyethylene or foam) is never connected directly to the boiler, even if it is singular, but only through a manifold (in common parlance, a comb). This allows you to install a separate circuit in each room, although there are situations when two pipes are laid on the floor of one room at once - this measure is necessary for a large area. The supply from the boiler goes to the manifold and the return goes from it to the heater. There are combs with shut-off valves, and some without them, but in any case it is possible to regulate the temperature - either with a tap or with a temperature sensor.
If necessary, to avoid confusion in the pipes, several boxes with collectors are installed in different rooms - this is very convenient in terms of temperature control during operation. Such containers, of course, are best recessed into the wall, but outdoor installation is also allowed - technologically, the location does not matter, it is simply a matter of aesthetics. As a casing for such a niche, plumbers often use metal boxes for built-in electrical panels - they are very convenient and reliable to use, and do not require painting. If the house does not have radiator heating and a gas boiler is installed, then it is better to give preference to a condensing unit - it is more expensive than a convection unit, but the cost will more than pay off during operation.
Combined heating

Combined heating scheme - radiators and heated floors
Modern residential buildings in the private sector, which have two and sometimes three floors, are equipped with combined heating, where radiators operate from one boiler together with a heated floor system. This option is very convenient to use, that is, warm floors themselves are more profitable and convenient than radiators, but they cannot be installed in every room. But, be that as it may, this choice is a personal matter for everyone and the reasons in this case do not matter - the most important thing here is the balance between different temperatures in the circuits.
If a minimum coolant temperature of 60-80°C is required in the radiator circuit, then in a heated floor system it will be 30-50°C, respectively, and all this must be done using one boiler from one supply. To do this, a three-way valve and a bypass are installed in front of the heated floor circuit (see diagram above). The valve is set to the desired temperature, for example, 40°C. Water from the supply flows into the pipe onto the floor until it exceeds this mark. When this happens, the valve switches and discharges hot water through the bypass into the return line. As soon as the floor temperature drops by 1-2°C, the valve switches again and supplies coolant to the floor circuit.
Conclusion
You can see for yourself that if you figure out in detail how to make heating yourself in a private house, then the question becomes not so difficult - the main thing is to correctly understand the technology. Of course, for this you will have to re-read the article more than once, and then the question of technology will arise, but this, as they say, is a gainful matter.
Work on arranging a heating system in a private house can be done independently if you have basic skills in working with tools and the tool itself, or you can order it from a specialized organization.
But, in any case, installing heating in a private house with your own hands begins with the theoretical part. You will need to decide which heating system wiring diagram you choose, how the coolant and boiler will circulate in it, and what brand will be installed in the system to heat the coolant.
Today, a person planning such work as installing heating pipes in a private house on his own, or installing a heating system, has the opportunity to choose one of the four most commonly used options for these purposes:
Variant of the radial heating system wiring method
The layout of the heating system in a private house, made according to the indicated option, has the following feature: the supply pipe is led to the highest point of the house (usually to the attic), here each pipe is supplied with its own beam.
We get a kind of sun with rays supplying hot coolant to the radiators. (Another analogy is a fountain).
Collector heating system
The heating pipe layout according to the specified option is classified as the most efficient and productive. The basis is a collector assembled in the attic, through the pipes of which the coolant is distributed. Correct routing of heating pipes and shut-off valves installed in the manifold allow, if necessary, to cut off any of the circuits without stopping the operation of the entire CO.
This system is considered the most convenient CO model. The coolant is supplied to the radiators through the collector. It also contains control elements, which makes it possible to regulate the temperature in any room, as well as replace and repair a failed unit without turning off the entire heating system.
A significant disadvantage is the high consumption of materials when installing CO according to the mentioned scheme, as well as the requirement for the mandatory installation of a manifold cabinet.
Heating wiring diagram for a private house, assembled using a single-pipe version

This option is quite simple to implement and will require minimal costs for the purchase of components and installation work. All this makes it today the most popular option for installing heating systems in private residential buildings and other facilities.
The heating pipe layout in this version allows the coolant to move sequentially from one heating device to another. Moreover, in each subsequent one, the temperature will be lower than in the previous one. Very often, the coolant reaches the last radiator at a low temperature, which is clearly not enough for heating.
Routing heating pipes in a house according to the specified version practically eliminates the possibility of adjusting the system, because blocked batteries do not allow the coolant to flow further. And if there is a need to repair any heating device, all the coolant is drained from such COs.
Two-pipe house heating system
It will cost significantly more than the previous version, and will require more time for assembly and adjustment. However, it will allow you to get serious gains in heating quality, system performance and efficiency.
Wiring heating in a private house with your own hands according to the specified scheme warms up the object much better. There are necessarily two pipes that are connected to each radiator. Correct routing of heating pipes ensures the following movement of the coolant. Hot coolant flows through the top, and cooled coolant is discharged through the bottom.
The advantage of the scheme: parallel connection of all heating devices. The heating wiring diagram for a private house according to the specified version allows you to repair a failed element without turning off the entire heating system.
Heating plan according to the method of coolant circulation in the system
In all currently operating COs, the coolant circulates according to one of the options listed below.
Natural circulation, another name - gravitational
The coolant in this case moves by using the difference in the density of the liquid having different temperatures. The hot one has a lower density, so it rises to the top of the system. The cold one is heavier, so it goes down.
In order to facilitate the movement of coolant in such systems, pipes are mounted at slight horizontal angles to promote gravity flow.
The main advantages of such a system are complete autonomy and maximum ease of assembly. Disadvantages: the need for a large number of large-diameter pipes. It is not possible to install modern models of radiators in such COs, which have small cross-sections and strict requirements for the slope of the main line.
Forced circulation
In this version, the coolant is moved by a running circulation pump. And its excess, formed when heated to high temperatures, is forced into the expansion tank.
In most options, CO tanks are closed, which ensures its protection from evaporation. Closed tanks are required to be used in systems where the coolant is any of the glycol solutions.
Such systems must be equipped with pressure gauges. When installing these systems, you will incur additional costs: you will need to buy thermostats, a pump, a pressure gauge, a tank, etc.
The advantages of the specified CO option, which the heating distribution of a two-story private house has according to the specified option: a minimum volume of coolant is required, smaller required pipe diameters, structurally implemented possibilities for adjusting the heating temperature of radiators, etc.
Disadvantage: Depends on availability of electricity to operate the pump.
Heating diagram based on wiring technique and piping arrangement
When choosing this version, it is better to entrust its installation to professionals, as it is quite complicated.
By type of installation there are:
- Horizontal CO. It is quite convenient in that it does not require the installation of risers for subsequent branching across existing premises.
- Vertical CO. They have no air pockets and are easy to install.
According to the direction in which the coolant moves, there are:
- Straight-through. The coolant moves from the boiler through the CO to the boiler.
- Dead-end. They move from the heat source in the opposite direction.
Heating schemes for a private house, the piping in which is carried out according to one of the above options, requires the performer to carry out high-quality preliminary calculations and carefully select the necessary equipment.
In the future, it will need to be mounted strictly according to the design diagram, otherwise the assembled CO may not work well.
How to choose the best heating layout for a private home?
When determining the required CO option, it is necessary to take into account several initial parameters:
- The total area of the room that will be heated by the specified system;
- Number of floors;
- The power of the heating boiler that is planned to be installed in the system;
- What coolant circulation scheme is planned to be used as a basis?
No matter how well the house is insulated, in our climatic conditions it is impossible to do without artificial heating. After all, in any case, there will be heat losses in winter, and they need to be replenished. Residents of apartment buildings don’t have much choice; heating is usually “included” and little can be changed. But in the private sector, the problems of designing and implementing a heating system are assigned to the homeowner. It is the owner who will be responsible for its management and maintenance. On the one hand, this is a burden: even if specialists are invited, you will have to figure out how to install heating in a private house, how the system is completed and functions. But it is also obvious that there is a huge plus, because the developer himself chooses the most suitable option for his conditions: type of fuel, heating device, wiring method.
Operating principle of a water heating system
There are systems where air acts as a coolant, or it is directly heated directly in the premises. We will talk about designs that use a liquid coolant (most often water), since the vast majority of our compatriots prefer them. The principle of operation is quite simple: the boiler heats the water, the water moves along a closed loop of pipes, through the surfaces of the radiators it gives off thermal energy to the air in the rooms, the water cools down and enters the boiler again - the cycle is repeated many times.
Water heating structure
All liquid heating systems have a similar set of elements:
The nature of coolant circulation
The liquid in the heating system can circulate naturally or forcefully. Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages; their choice significantly affects the functionality of the system:
- Forced circulation is carried out by an electric pump, which is mounted on the return or supply pipe. The increased pressure in a closed system allows for high-quality heating of large houses, including several levels, while the temperature regime will be very easy to regulate.
- Natural circulation (gravitational system) occurs due to the fact that heated and cooled water differs in density. These are open systems with normal pressure; electrically dependent devices are not used here. This option is well suited if the power supply in the village is unstable or absent.

Gravity systems are often supplemented with a circulation pump connected via a bypass (in parallel). This is how you get effective universal heating, which will also work if the cottage loses power
Features of heating installation in a private house
Since heating a house is always difficult, you can’t start without design. Schemes and plans on paper are only the visible part of the iceberg, the tangible result of an engineer’s work. In order for heating to be effective, it is necessary to accurately determine the amount of heat that the house will lose during the winter. Then draft versions of the system are developed and hydraulic calculations are made, which will help you select the right equipment, choose the cross-section of pipes and the wiring method. Naturally, specialists should be puzzled by such problems, while the developer can at this time deal with other issues, for example, obtain permits for tapping into a gas main.

A competent calculation will help to rationally distribute the thermal output of the boiler across all rooms. Indicators of local hydraulic resistance and coolant flow are always taken into account
What is needed to connect a gas boiler
The required power of the heating device is determined at the design stage. The boiler must provide enough heat to compensate for its losses through the enclosing structures. You can focus on the figure of 1 kW of power for every ten square meters of building area in the climate of central Russia. Of course, we are talking about a house with good thermal insulation.
Note! Boilers can not only provide space heating, but also provide hot water for domestic needs. There are two solutions: buy a double-circuit device, or install an indirect heating storage tank in a system with a single-circuit boiler.

The indirect heating tank does not have heating elements; the water temperature rises due to a heat exchanger coil connected to the heating.
In private houses, if necessary, a separate room is equipped for heating devices - a boiler room, where, in addition to the heat generator, auxiliary elements are also located. This may be especially relevant if the heating configuration requires the presence of a floor-standing boiler, which, for normal circulation, in a gravity system when located on the ground floor, must be installed in a pit. Note that modern wall-mounted models are compact and beautiful; they can be installed in any room, for example, in the kitchen.
To connect a gas boiler, you need to take care of connecting it to electrical power and water pipes (cold supply, outgoing DHW branch). Naturally, somewhere nearby there should already be a gas pipe with a tap at the outlet. As for the chimney, it is not at all necessary to lead the pipe through the ceiling to the roof; for turbocharged gas boilers, you can use a coaxial chimney passing through the outer wall.
Note! In the room where the boiler is located, it is necessary to install a gas leak detector.
How to install pipelines
Pipes connect radiators to boilers; as a rule, we can observe a kind of tree, where the main circuit, like a trunk, is made with a large diameter, and thinner pipes for connection extend from it to the radiators. In complex systems, pipes of 3-4 different diameters can be used, which allows the optimal amount of coolant to be supplied to different parts of the system, while saving on materials immediately and on energy during operation.

This diagram shows the gradation of diameters common for private houses
Selecting material for heating pipes
Metal pipelines are good for their strength and stability of linear dimensions when heated. Conventional steel is rarely used lately, as it is too susceptible to corrosion damage, and deposits quickly accumulate in such pipes. Stainless steel and copper are an order of magnitude more practical, but developers are understandably put off by the high cost of materials, as well as the complex technology for assembling such pipelines.
Polymer pipes are much easier to install, largely because of this, polypropylene has become especially popular, which almost all home craftsmen have learned to solder. Pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene are assembled using press fittings; for this you need to have special expensive equipment, but it can be rented - the technology itself is not complicated. In terms of physical properties, something between metal and polymer samples is a metal-plastic pipe, which is assembled on threaded fittings.
Plastic pipes are cheaper than metal ones, they are more durable and have less hydraulic resistance. Disadvantages include greater thermal expansion of polymers and the risk of mechanical damage.
Note! To create heating systems, it is necessary to use polypropylene pipes with internal reinforcement. This can be an additional foil shell (it is cleaned at the edges before soldering), or an inner layer of fiberglass.
Several ways to install heating pipes in a cottage
The first thing you have to choose is the presence/absence of separate supply and return. According to this principle, the following types are distinguished:
- Two-pipe heating has a separate supply and separate return pipeline. The radiators here are easily adjustable and independent of each other; the system copes well with its tasks in a house of any size.
- Single-pipe heating has only one ring (performs the functions of both return and supply). It is somewhat cheaper, but it is advisable to use it only in small houses where there are few heating devices. The main consumer disadvantage of such configurations is that the last radiator is noticeably cooler than the first.

In two-pipe systems, each radiator is supplied with a carrier of approximately the same temperature
Heating pipelines can be routed both along the floor (for example, in a screed or between joists) and in the ceiling area (including in the attic). If the heating is assembled carefully, the pipes will look good, even if they are laid openly along the walls.
In private houses, horizontal wiring is almost always implemented. Vertical schemes with top filling (the supply pipeline, leaving the boiler, rises and stretches at the top of the building), where there are risers, can be used in cottages on several levels, but they require more capital investments.
Heating devices in the heating system of a private house
Traditionally, we use radiators for heat exchange, which, as a rule, are mounted under the windows. Here they interact with the cold air descending from the window openings and create convective movement of air masses.

Depending on the piping method, the efficiency of the radiator will vary
The larger the surface area of a radiator, the more heat it can give off. By assembling a radiator from a different number of sections, we can make a heating device of the required power. But the performance of batteries also depends on the material; for example, aluminum and bimetallic models are considered the most productive.
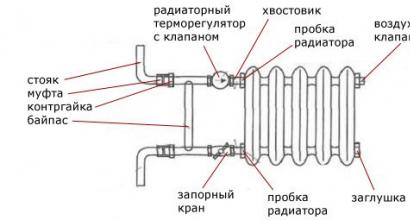
Note! To regulate heat transfer, radiators are equipped with special devices. They can be controlled manually, but there are also automatic devices that change the intensity of the flow in response to the air temperature in the room.
There are several options for piping radiators. If the side connection is mainly used if you need to install heating in an apartment with risers, then the diagonal and bottom connection is more typical for the private sector, where horizontal piping is common. Diagonal strapping has proven itself well with large batteries. The lower one is the least efficient among other types, but in closed systems with a circulation pump it works well and, moreover, is the most convenient for installation.
Note! If a single-pipe heating system is chosen, it will be much more efficient and functional if the radiators are connected parallel to the pipeline. This is the only way to balance the system.

To implement a parallel connection, leave a section of the main ring that will allow coolant to pass through even if the taps on the heating device are completely closed
We can talk for a long time about how to properly conduct heating in a private house, but still many important nuances will remain in the shadows. Meanwhile, the cost of an error here is too high, and little things simply do not exist. That is why we strongly recommend using the help of professionals as much as possible, especially in terms of designing and tying up equipment.
Video: do-it-yourself heating scheme for a private house
In order for your stay in a private house to be as comfortable as possible, it must certainly have such an important element as a heating system for a private house. Only with its help can you create surprisingly pleasant, comfortable living conditions.
Of course, the coolant plays an important role in any heating system. In fact, its presence is a prerequisite, otherwise the heating device in a private house simply will not be able to function efficiently. Almost all modern heating systems use water as a coolant.
Heating system of a private house
The most correct option is to contact a specialized company, whose employees will help you choose a heating system for a private home and provide installation services for heating systems.
Professionals will be able to advise which type of heating system will be most efficient to use in your home, and will install it correctly.
It should be noted that sometimes home owners, not wanting to hire additional specialists, take on the installation of the heating system themselves. In fact, there is nothing complicated about this - you just need to follow certain installation rules.
What does the heating system consist of?
Quite often, the heart, the main element of any heating system is the boiler. It is he who heats the coolant, the task of which is obvious - to spread heat throughout the house. And, of course, liquid can best cope with this task. In most heating systems, it is customary to use water as a coolant.
A system with a coolant of this type is made closed. That is, the water in it circulates around the ring, and adding coolant is required extremely rarely.
Today, the two-pipe heating system, which is shown in the photo, is recognized as the most reliable and practical:

It consists of two circuits closed on the boiler - coolant supply and return. The first serves to supply the liquid heated in the boiler to the radiators, where it gives off its heat. After cooling, the coolant returns through the return pipes to the boiler for reheating. In this case, the most rational and most effective is the parallel arrangement of radiators - thus, they warm up at the same time, which makes it possible to uniformly warm up all rooms. It is important to remember that the heating efficiency is affected by the distance between the coolant supply and return circuits. The permissible minimum is the height from the window sill to the floor.
Many experts argue that such a heating system is less efficient than the old stove heating.
It should be admitted that they are partly right - after all, due to the passage of coolant through pipes and components, a certain loss of coolant occurs. However, we should not forget that stove heating does not make it possible to heat all rooms evenly at the same time. In addition, using a stove is very inconvenient due to the need to store a large supply of firewood. If you use a wood-burning boiler, much less fuel is required.

Most often, a fairly simple and at the same time very effective two-pipe heating system with natural coolant circulation is used. It allows you to heat your house with high quality without using additional equipment - electric circulation pumps. The reason for the popularity of this heating system for private houses is explained by the fact that there are frequent cases of power outages - and in this case (without electricity), the system simply will not be able to work.
All that is necessary for the correct and highest quality operation of such a heating system in a private home is strict adherence to the rules during its installation and a supply of fuel.
One of the main requirements, which is extremely important to comply with for the further operation of the system, is to create the maximum possible difference in height between the outlet of the system and the highest point of the system. That is why the most rational option is to locate the boiler with a pipe in the basement. If there is no basement, the boiler is installed in a recess on the ground floor. No less important is the creation of a slope for the return line. It is performed horizontally, starting from the first radiator of the system.

In a heating system of this type, there is one more mandatory element - an expansion tank. It is used to create maximum pressure in the system, which is extremely important for normal circulation. The operation of the tank is based on the usual gravitational principle. It should be placed as high as possible - the ideal place would be the attic. It is the height of the location, and not the amount of liquid in the tank, that determines the pressure.
The tank should have a medium volume. After all, its additional function is the ability to control the coolant level, which, if necessary, can simply be drained from the tank.
It should be remembered that such heating systems for a private home can only operate correctly if the coolant is water. A system with this principle of operation of the expansion tank is called open.

Closed systems are those in which the expansion tank is in no way connected to the outside world. That is, it does not have the ability to pump out coolant. In such a system it is customary to use a compensation tank. This is a small container, the internal cavity of which is divided into two parts by a flexible membrane. One of the parts is filled with coolant. The pressure in the system is regulated by bending the membrane in one direction or another. Since the system is closed, this allows antifreeze to be used as a coolant.
Pipes for heating system
For a long time, exclusively steel pipes were used to create the heating system. This was quite inconvenient, since installation took a long time, and rough seams subsequently greatly spoiled the visual perception of the system and the types of heating of private houses.
Fortunately, today it is possible to install a heating system of any complexity using metal-plastic pipes. They are thinner and more flexible. Their surface is made of special heat-resistant plastic, and the inside is made of a thin layer of aluminum. There are a huge number of additional elements on the market for metal-plastic pipes - corners, connections, taps. They allow you to both connect pipes to each other and connect a different type of pipe to them.

Since today there are quite a large number of types of metal-plastic pipes, special attention should be paid to the markings when choosing them. Pipes intended for heating systems are marked with the symbols “PE-RT-AL-PE-RT”.
The advantage of metal-plastic pipes is that they are quite easy to work with. Quite flexible and lightweight, they can be cut with a regular hacksaw or metal scissors.
In order for the heating methods of a private home to be as airtight as possible, all components should be carefully installed. In this case, it is rational to use press fittings - they perfectly preserve the integrity of the pipe.
What should you do first?
So, you have decided to create a high-quality and reliable heating system in your home that works with liquid coolant. The first thing that needs to be done when planning any type of heating systems for a private home is to create a detailed plan, a diagram of the future system. It should indicate: the location and level of the boiler, the duration of the pipeline, the placement of radiators and all additional components of the system, up to Mayevsky taps. After this, you should determine what kind of boiler power you need. After all, a weaker one will not be able to create the required level and rate of heating. And it is simply irrational to use a stronger one - after all, it will only work at half its power.

Quite often, homemade heating boilers are used when creating a heating system. They have a lower cost, but it is impossible to determine their exact power.
If you decide to supplement the types of heating systems in a private home with just such a boiler, then you should simply calculate the maximum volume of coolant that this boiler can hold. To do this, simply divide the volume of the room (or the total volume of the premises) that will be heated by 1000. That is, the volume of a room of 100 m2 is equal to 300 m3. We divide this indicator by 1000 and get 300. Accordingly, this is the amount of coolant that a homemade boiler should contain.

It should be noted that the size of the boiler directly depends on its power. That is, the higher the power, the larger the boiler. Of course, before creating a heating system plan, you should find an ideal place where the boiler installed will not disturb anyone. In this case, the level of the boiler’s location should be taken into account - it should be the lowest point of the system. The ideal solution is to locate the boiler in the basement. If your house does not have a basement, take care of a convenient niche in the floor. It is advisable that the boiler be located in a separate room, access to which can be limited for security reasons.
It is important to understand that certain types of boilers (gas, electric boilers) require special placement conditions. If you don’t know anything about them, be sure to contact specialists for advice before installing the system.
What to consider
When installing the main line, you should take pipes whose diameter is twice as large as the pipes that will supply the coolant directly to the radiator. This rule applies to both supply and return pipes. When installing the pipeline, the pipes must be secured with special rings - this way you can get rid of sagging.

Even if the system consists of metal-plastic pipes, the vertical riser running from the heating boiler to the expansion tank must be made of steel pipe. If there is no tank, the first few meters of the pipe should be made of steel. When connecting a membrane expansion tank, you can use a pipe of smaller diameter.
This is because the intense heat rising from the boiler can damage the plastic part of the pipe. It is better that the metal-plastic pipe is located only in a heated room.

If possible, you can lay two heating circuits, each of which, in turn, will consist of supply and return pipes. Such heating options for a private home are undoubtedly more expensive. However, if repairs become necessary, one of the circuits can be closed.
Air bleed valves must be installed on each radiator, as well as on the coolant supply and return lines.
Its excessive accumulation in the system can cause serious damage. The installation of radiators should be carried out in compliance with one condition - the side from which the return pipe exits should be located slightly lower - this is necessary in systems with natural coolant circulation.

When using a homemade heating boiler, it should be taken into account that the direct line pipe should be located as high as possible. This will avoid destructive water hammer. The heating boiler should be installed with a slope of 5 mm, which should be made towards the return line.
Rules for operating the heating system
When the installation of the system is completely completed, it should be filled with coolant. In this case, all valves that are used to bleed air must be open. After the heating systems of a private home are filled with coolant, the boiler should be lit using a small amount of fuel. This makes it possible to check the uniform heating of the system - there should be no excessively hot or cold areas (in this case, open the radiator valve and drain the water until hot water flows out).
There should be no extraneous sounds when heating in the boiler. Minor leakage of coolant in the area of threaded connections is allowed.
After several test runs, the threaded connection stops letting water through. Then you can start heating the boiler at full power.
Boiler power is a very important indicator that must be selected correctly. If the power is higher, there is a possibility of the boiler boiling, which, in turn, can lead to the most dire consequences not only for the heating system, but also for the entire house. If the boiler power is too low, this affects the return temperature level - it does not exceed 40 degrees.
Properly installed working heating methods for a private home should not produce any extraneous sounds. In addition, the temperature difference between the supplied coolant and the return does not exceed 40 degrees. A video on how to install the system can be viewed below.